Create A Budget Tracker in HTML CSS & JavaScript
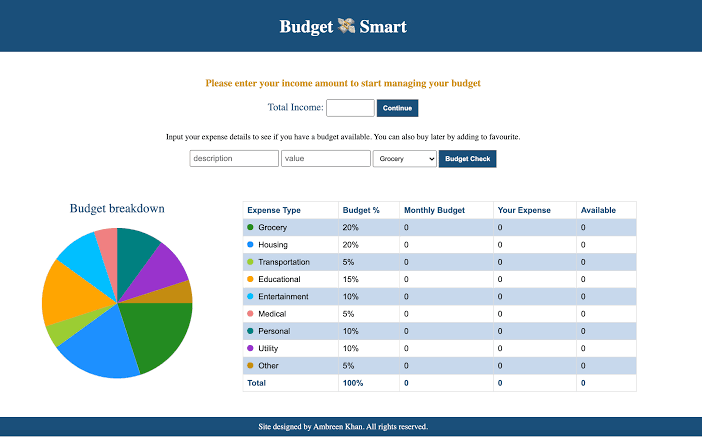
Creating a budget tracker with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript involves building a simple interface where users can add income and expenses and view their budget status. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to create a basic budget tracker.
HTML Structure
Create an HTML file with the necessary structure for the budget tracker.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Budget Tracker</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Budget Tracker</h1>
<div class="budget-display">
<div id="income">
<h2>Income</h2>
<p>$<span id="income-amount">0.00</span></p>
</div>
<div id="expenses">
<h2>Expenses</h2>
<p>$<span id="expenses-amount">0.00</span></p>
</div>
<div id="balance">
<h2>Balance</h2>
<p>$<span id="balance-amount">0.00</span></p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="transaction-form">
<h2>Add Transaction</h2>
<form id="transaction-form">
<label for="type">Type:</label>
<select id="type" required>
<option value="income">Income</option>
<option value="expense">Expense</option>
</select>
<label for="description">Description:</label>
<input type="text" id="description" required>
<label for="amount">Amount:</label>
<input type="number" id="amount" step="0.01" required>
<button type="submit">Add Transaction</button>
</form>
</div>
<div class="transaction-list">
<h2>Transaction History</h2>
<ul id="transaction-history"></ul>
</div>
</div>
<script src="scripts.js"></script>
</body>
</html>CSS Styling
Create a CSS file (styles.css) to style the budget tracker.
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.container {
max-width: 600px;
margin: 2rem auto;
padding: 2rem;
background-color: white;
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
text-align: center;
}
h1 {
margin-bottom: 1rem;
}
.budget-display {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
margin-bottom: 2rem;
}
.budget-display div {
width: 30%;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
padding: 1rem;
border-radius: 8px;
}
.transaction-form, .transaction-list {
margin-bottom: 2rem;
}
form label, form input, form select, form button {
display: block;
width: 100%;
margin: 0.5rem 0;
padding: 0.5rem;
}
form button {
background-color: #333;
color: white;
border: none;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 4px;
}
form button:hover {
background-color: #555;
}
.transaction-list ul {
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
}
.transaction-list li {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
padding: 0.5rem;
border-radius: 8px;
margin-bottom: 0.5rem;
}
.transaction-list li.income {
border-left: 5px solid green;
}
.transaction-list li.expense {
border-left: 5px solid red;
}JavaScript Functionality
Create a JavaScript file (scripts.js) to add the functionality to the budget tracker.
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() {
const transactionForm = document.getElementById('transaction-form');
const transactionHistory = document.getElementById('transaction-history');
const incomeAmount = document.getElementById('income-amount');
const expensesAmount = document.getElementById('expenses-amount');
const balanceAmount = document.getElementById('balance-amount');
let income = 0;
let expenses = 0;
transactionForm.addEventListener('submit', function(event) {
event.preventDefault();
const type = document.getElementById('type').value;
const description = document.getElementById('description').value;
const amount = parseFloat(document.getElementById('amount').value);
if (type === 'income') {
income += amount;
} else {
expenses += amount;
}
updateBudgetDisplay();
addTransactionToHistory(type, description, amount);
transactionForm.reset();
});
function updateBudgetDisplay() {
incomeAmount.textContent = income.toFixed(2);
expensesAmount.textContent = expenses.toFixed(2);
balanceAmount.textContent = (income - expenses).toFixed(2);
}
function addTransactionToHistory(type, description, amount) {
const transactionItem = document.createElement('li');
transactionItem.classList.add(type);
transactionItem.innerHTML = `
<span>${description}</span>
<span>$${amount.toFixed(2)}</span>
`;
transactionHistory.appendChild(transactionItem);
}
});This example demonstrates how to create a simple budget tracker using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. The application includes:
- HTML: Structure for the tracker, including forms for adding transactions and displaying budget information.
- CSS: Styling for a clean and user-friendly interface.
- JavaScript: Functionality to handle adding transactions, updating the display, and maintaining a transaction history.
This basic setup can be further enhanced by adding features such as persistent storage using localStorage, more detailed budget categories, and data visualization for better budget tracking.